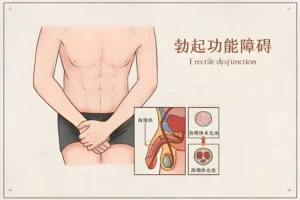
Sexual dysfunction doesn’t just impact the quality of a couple’s intimate life — it can also place a heavy burden on a man’s mental health. From physiological and psychological factors to lifestyle habits and environmental exposures, multiple elements can work together behind the scenes to cause sexual decline. Let’s break it down clearly.
✅ Physiological Causes: The Body’s Internal Alarm
- Chronic Diseases Conditions such as hypertension and diabetes damage vascular endothelial cells, impairing blood flow to the penis and leading to erectile dysfunction. High cholesterol can cause atherosclerosis, restricting blood supply to the genitals and reducing both erection strength and duration.
- Hormonal ImbalancesTestosterone is key to male sexual function. Disorders such as hypothyroidism or pituitary gland dysfunction can lower testosterone levels, resulting in reduced libido and difficulty achieving erections. Overactive adrenal glands can also disrupt hormone balance, further affecting sexual performance.
- Urogenital Infections Inflammatory conditions like prostatitis or seminal vesiculitis may cause nerve pain and interfere with normal sexual response. Recurrent infections such as urethritis or epididymitis can also affect ejaculation, potentially leading to premature ejaculation or anejaculation.
- Nervous System InjuryPelvic fractures or lumbar disc herniation may compress nerves involved in sexual function. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption or smoking can damage nerve transmission and delay sexual response.
✅ Psychological Causes: The Invisible Emotional Burden
- Chronic Stress Work pressure, financial burdens, and prolonged mental stress can keep the brain in a state of tension, suppressing sexual arousal centers and leading to reduced libido or ED.
- Anxiety & Depression Negative emotions interfere with neurotransmitter activity. For example, serotonin imbalance is linked to premature ejaculation or difficulty ejaculating. Long-term depression may also lower testosterone levels and reduce sexual drive.
- Psychological Trauma Past sexual failures or relationship conflicts can create mental blocks during intimacy, reducing erection quality. Excessive guilt, shame, or low self-esteem can further suppress sexual desire and response.

✅ Lifestyle Factors: The Hidden Impact of Daily Habits
- Poor Diet A diet high in fat, sugar, and salt can lead to obesity and vascular damage, limiting blood supply to sexual organs. Deficiencies in trace minerals such as zinc and selenium can also reduce sperm quality and testosterone production.
✅ For daily support, men may benefit from drinking herbal teas that nourish the liver and kidneys and boost energy, such as: 👉
- Sedentary Lifestyle Sitting for more than 8 hours a day can compress the prostate and pelvic vessels, impairing blood flow and increasing the risk of chronic prostatitis, which negatively affects erection and ejaculation.
- Sleep Deprivation Chronic late nights and irregular sleep disrupt circadian rhythms, reduce testosterone production, and weaken immunity. Fatigue also leaves men with low stamina during sex.
- Excessive Smoking & DrinkingNicotine causes blood vessel constriction, reducing penile blood flow. Alcohol depresses the central nervous system, interfering with sexual arousal, and chronic drinking can damage the liver, disrupting estrogen metabolism and hormonal balance.
✅ Environmental & Medication-Related Risks: Often Overlooked Triggers
- Environmental Toxins Long-term exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, or industrial chemicals can disrupt endocrine function and damage reproductive cells. Excessive heat exposure from saunas or hot baths can impair spermatogenesis, indirectly impacting sexual performance.
- Medication Side Effects Some drugs — such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, sedatives, and sleeping pills — may suppress the central nervous system or disrupt hormone levels, resulting in ED or loss of libido. Chronic corticosteroid use can even cause testicular atrophy.
Sexual dysfunction is often the result of a combination of these factors. If you notice persistent symptoms, it’s important to visit a professional urologist or men’s health specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and targeted treatment.